Solve Your Residential Water Problem with Diamond H2O
Do you know what's in your water? This page will help you find out!

Hardness (Scale)
Symptoms:
White Scale formation in: piping, water heaters, dishwashers, sinks, showersetc.
– piping
– water heaters
– dishwashers
– sinks
– showers
EPA MCL: N/A
All Water Softeners |
Rustmaster |
DTRS |
Industrial Water Softeners |
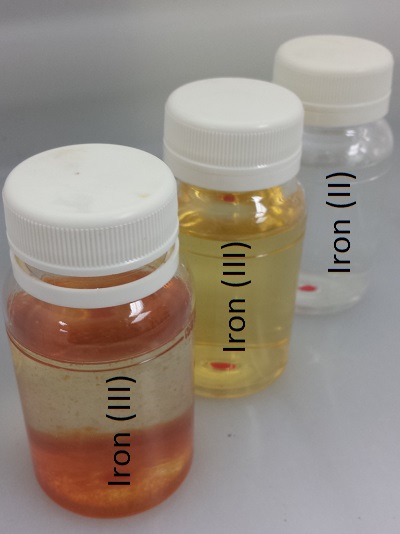

Iron (Staining)
Symptoms:
– Metallic Taste in Water
– May combine with Tannins in Tea to/coffee/wine to create gray to black appearance.
– Red or Orange Staining in sinks, bathroom fixtures, and laundry.
EPA SMCL: 0.3 mg/L
Liberator IR |
Rustmaster |
DTRS |
Refiner AN |
Liberator AN |
Note: Iron is present in two forms and caution must be used when choosing a system.
Tannins (Staining)
Symptoms:
– Yellow/Brown Staining.
EPA SMCL: N/A
DTRS |

Low pH (Acidity)
Symptoms:
– Corrosion
– Blue Staining (from copper pipes & fixtures)
– Rust Staining (from iron pipes & fixtures)
Potable Water Range: 6.5 to 8.5
Refiner AN |
Liberator AN |

Iron Bacteria
Symptoms:
– Slimy substance in toilet tanks and/or pipes
– Discoloured and/or bad tasting water.
– Red or Orange Staining in sinks, bathroom fixtures, and laundry.
– Musty Odor
EPA SMCL: N/A
Liberator OR |

Manganese (Staining)
Symptoms:
– Metallic Taste in Water
– May combine with Tannins in Tea to/coffee/wine to create gray to black appearance.
– Red or Orange Staining in sinks, bathroom fixtures, and laundry.
EPA SMCL: 0.05 mg/L
Liberator IR |
Rustmaster |
DTRS |
TDS
Symptoms:
– May cause spotting/scale.
– Undesirable Taste
EPA SMCL: 500 mg/L
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |

Chlorine & Chloramines (Taste/Odor)
Health Effects:
– eye/ nose irritation, stomach discomfort
Symptoms:
– Chlorine taste/odor
EPA MCL: 4.0 mg/L
Liberator AC |
Refiner AC |
Diamond Dual |
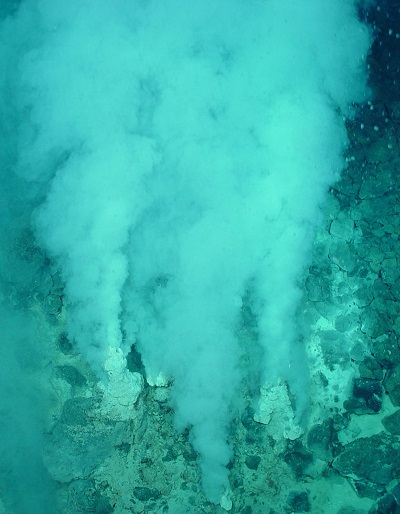

Hydrogen Sulfide (Rotten Egg Odor)
Symptoms:
– Rotton Egg taste/odor
EPA MCL: N/A
Liberator OR |
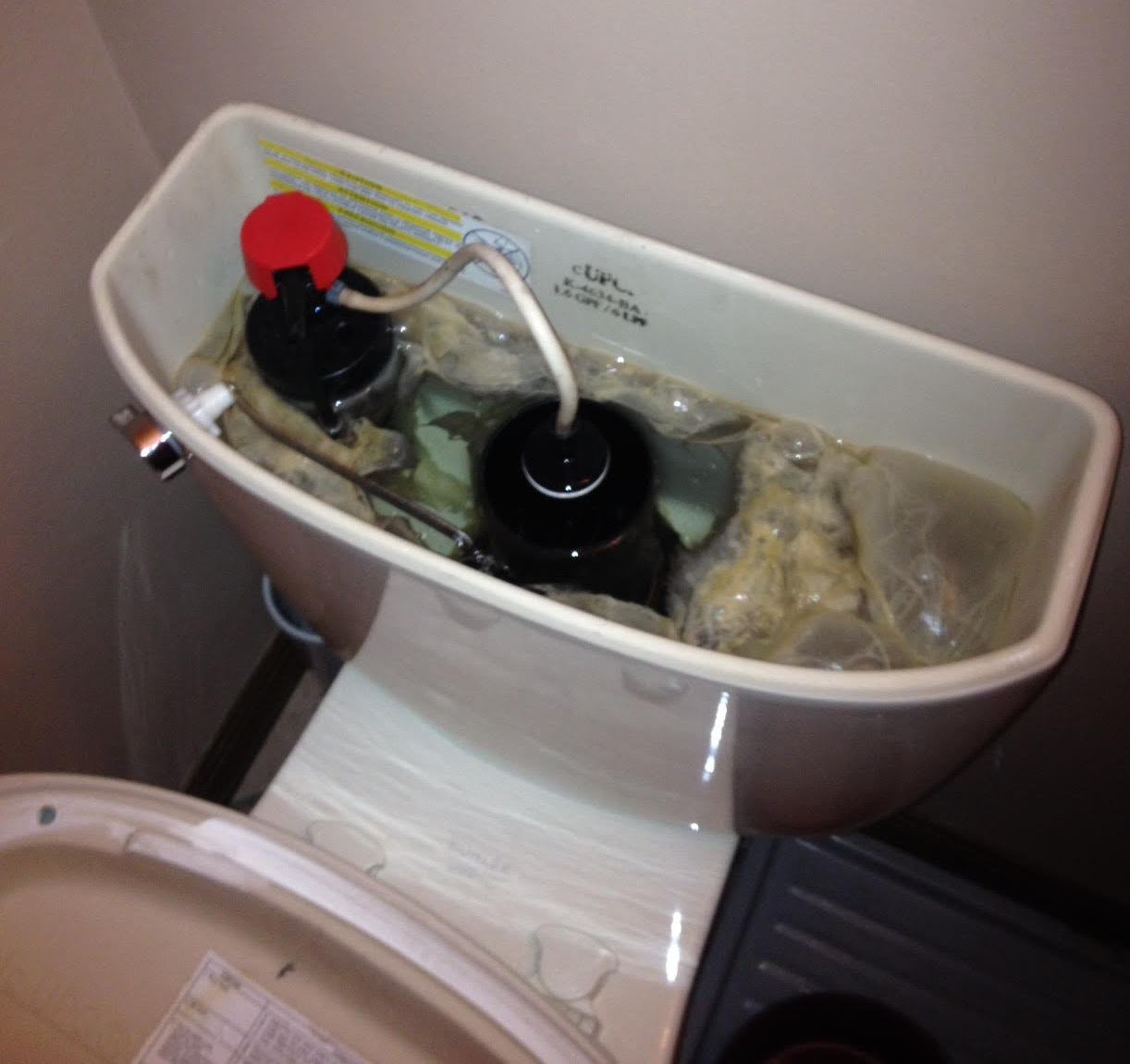

Sulfur Bacteria
Symptoms:
– Slimy substance in toilet tanks and/or pipes
– Discoloured and/or bad tasting water.
– Rotten Egg Odor
EPA SMCL: N/A
Liberator OR |
Chloride (Salty Taste)
Symptoms:
– Salty Taste
– Stainless Steel Corrosion
EPA SMCL: 250 mg/L
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |
Sulfate (Salty Taste)
Symptoms:
– Salty Taste
– Concentrations over SMCL may have laxative effects
EPA SMCL: 250 mg/L
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |
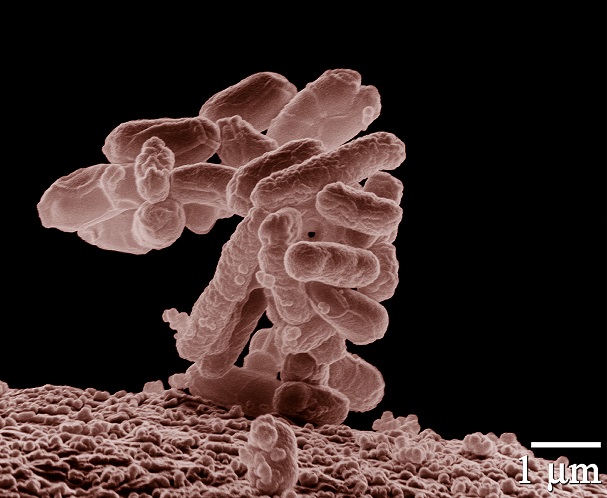
Total Coliforms (including fecal coliform and E. Coli)
Health Effects:
Not a health threat in itself; it is used to indicate whether other potentially harmful bacteria may be present
EPA MCL: 1 cfu
Shocking the well. Contact us for more information.
Arsenic
Health Effects:
Skin damage or problems with circulatory systems, and may have increased risk of getting cancer
EPA MCL: 10 µg/L (0.01 mg/L)
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |
Lead
Health Effects:
Infants and children: Delays in physical or mental development; children could show slight deficits in attention span and learning abilities Adults: Kidney problems; high blood pressure.
EPA MCL: 15 µg/L (0.015 mg/L)
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |
Copper
Health Effects:
Short term exposure: Gastrointestinal distress
Long term exposure: Liver or kidney damage. People with Wilson’s Disease should consult their personal doctor if the amount of copper in their water exceeds the action level
EPA MCL: 1.3 mg/L
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |
Nitrate
Health Effects:
Infants below the age of six months who drink water containing nitrate in excess of the MCL could become seriously ill and, if untreated, may die. Symptoms include shortness of breath and blue-baby syndrome.
EPA MCL: 10 mg/L
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |
Nitrite
Health Effects:
Infants below the age of six months who drink water containing nitrite in excess of the MCL could become seriously ill and, if untreated, may die. Symptoms include shortness of breath and blue-baby syndrome.
EPA MCL: 1.0 mg/L
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |
Fluoride
Health Effects:
Bone disease (pain and tenderness of the bones); Children may get mottled teeth.
EPA MCL: 4.0 mg/L
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |

Low pH (Acidity)
Symptoms:
– Corrosion
– Blue Staining (from copper pipes & fixtures)
– Rust Staining (from iron pipes & fixtures)
Potable Water Range: 6.5 to 8.5
Refiner AN |
Liberator AN |

Chloride (Salty Taste)
Symptoms:
– Salty Taste
– Stainless Steel Corrosion
EPA SMCL: 250 mg/L
Clear Flo Free Standing Series |
Clear Flo Hinged Wall Mount Series |
Element Series |
Microline |

